The Commonwealth Ensigns
In February 1903 it was announced in the Commonwealth Gazette that King Edward VII had approved the design for the Flag of Australia.
- The Commonwealth Blue Ensign
- The Commonwealth Red Ensign – for the merchant Navy.
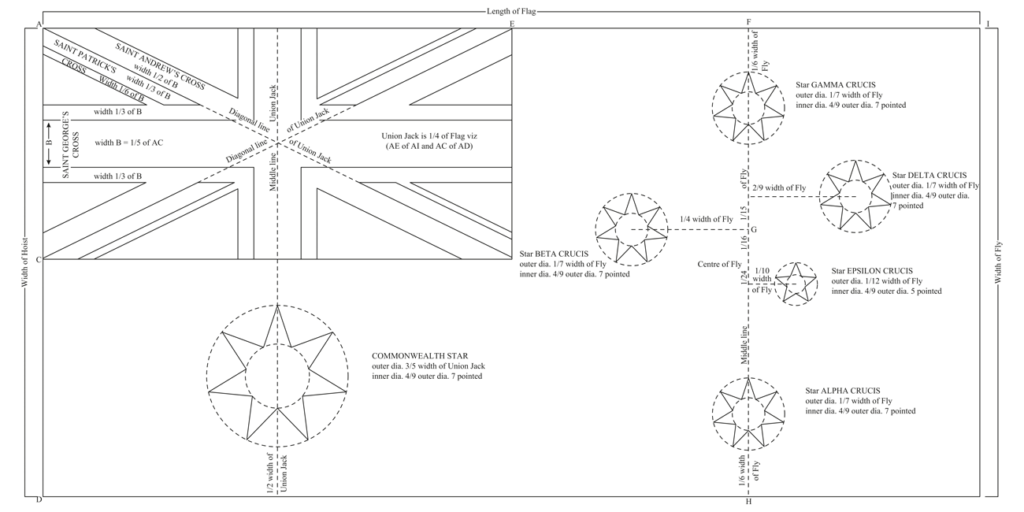
On both ensigns the stars of the Southern Cross were simplified to four seven-pointed stars and one five-pointed star. In 1908 a seventh point was added to the Commonwealth star to represent the Australian territories.
However, people were confused about the use of two Australian flags. The blue ensign was meant for official and naval purposes and the red ensign was meant to be used by the merchant fleet, but the general public began using the red ensign on land.
The Flags Act 1953
In 1941, Prime Minister the Rt Hon Robert Menzies issued a press statement recommending the flying of the blue ensign as a national emblem. The flags Act 1953 was passed by Parliament and was one of the few Commonwealth Bills signed by the Monarch rather than the Governor-General. This document was signed by Queen Elizabeth herself during the 1954 Royal Tour of Australia. The Australian blue ensign was now the Australian National Flag and the Australian Red Ensign as a flag for merchant ships registered in Australia.
Her Majesty’s signature would validate the transition in national flags which was taking place, from Union Flag to the Australian National Flag.
In 1998 an amendment was passed to ensure that the Australian National Flag can only be changed with the agreement of the Australian people.
The Commonwealth Flag Network
You can register for the Commonwealth Flag Network for up-to-date advice on how to fly the flag on special occasions. After registering you will receive an email at the same time as flag marshals around the country. Follow the link: nationalsymbols@pmc.gov.au.